What is Smart Agriculture?
Smart agriculture is often associated with the use of IoT in agriculture. The aim is to manage farms more precisely and efficiently. This includes monitoring the irrigation of plants in many facets and monitoring animals, machines and Facilities. A growing aspect is the environment, which is of particular importance in times of climate change and resource efficiency is becoming an increasingly important issue. Site-specific data can be used to make sustainable decisions and improve animal and plant welfare at the same time. Even smaller organic farms can solve their requirements cost-effectively with IoT technologies such as LoRaWAN or NB-IoT.
Smart agriculture IoT solutions are not only used in agriculture, often referred to as smart farming. Beyond traditional agriculture, the applications are finding applications in various areas that focus on the efficiency, sustainability and optimization of the food supply chain and related systems. Others, however, transition smoothly into applications for Smart Villages and Smart Cities , especially monitoring the immediate environment.
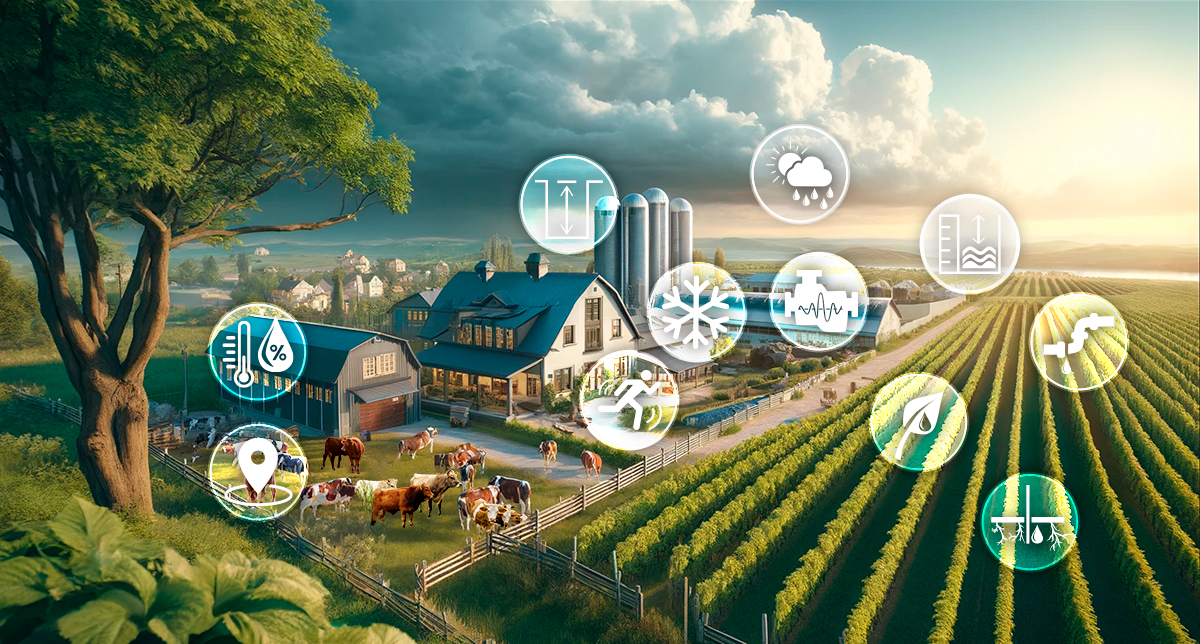

IoT solutions for smart agriculture
Are you ready to explore the possibilities of Smart Agriculture?
Discover the diversity of smart agriculture far beyond the fields. Whether it's urban green spaces, water management or sustainable city plans, we have the technology to help you move forward. Do you have a specific use case in mind? Share your vision with us and together we can create innovative solutions for a sustainable future. Get in touch with us today!
What is the difference between smart agriculture and smart farming?
Smart farming focuses specifically on agricultural production. By using IoT products such as soil sensors, weather stations, the pH value and networked irrigation systems, farmers can collect and analyze precise data about their fields. This data enables more precise control of cultivation and production processes, from sowing to irrigation and harvesting. The aim is to maximize yields, optimize the use of water and fertilizers and at the same time minimize the environmental footprint of agricultural activities. Smart farming as a sub-aspect of smart agriculture uses the advantages of IoT technology to promote more efficient and sustainable agriculture.


Smart agriculture uses sensors and actuators beyond traditional agriculture to improve efficiency, productivity and sustainability in various areas. This not only includes farms, but also extends to the monitoring and management of urban green spaces, parks and other non-agricultural environments. By integrating IoT, it becomes possible to collect and analyze a variety of data about the environment. This information enables optimized irrigation and efficient maintenance and care of urban and rural green spaces. Smart agriculture leads to better resource efficiency and minimizes environmental impact, which flows seamlessly into sustainable smart city concepts.
Who benefits from smart agriculture?

Farms
Agriculture benefits enormously from smart agriculture and the integration of IoT technologies, as they enable more efficient and sustainable farming. IoT technologies such as LoRaWAN and NB-IoT can make full use of their enormous reach. Whether it is a data-based, optimized irrigation and fertilization strategy, monitoring the weather and the environment or very specific values such as temperature and humidity in greenhouses or leaf moisture. IoT has a lot to offer the agricultural sector.

Garden and landscape maintenance
Precise monitoring of soil moisture and soil quality using IoT sensors enables targeted irrigation and fertilization. Additional automated irrigation systems reduce water consumption based on real-time data. It also reduces labor and supports healthy plant development. Depending on the system, the monitoring of liquid levels or visitor flow measurements can also be of interest.

Tiny Farms
Tiny farms, sometimes also called micro farms, refer to the general trend towards smaller, innovative farms that use efficient farming methods and technologies. The focus is often on resource efficiency and sustainability. These can include vertical farming, container gardens or hydroponic systems, which are particularly space-saving. However, smaller farms, often organic farms, are also increasingly supplying the local population with fresh produce.

Forestry and forest management
Forestry and forest management face the complex challenge of forest conversion and the growing risk of forest fires. Smart Agriculture offers innovative IoT solutions to support these challenges. They do not prevent the impact on forests, but they provide valuable information in real time to react earlier with a minimization of human intervention.
IoT expertise for your smart agriculture project
Whether it's an initial consultation, further development or long-term support, our IoT experts are at your side. It's up to you whether you want a product recommendation for a soil moisture sensor or an IoT consultant for planning. You will find the right IoT services with us.
High added value through resource efficiency with digital farming
Digital farming enriches agriculture by using IoT technologies and intelligent data analysis to enable high added value through increased resource efficiency. A key element here is the monitoring of soil moisture, which enables precise irrigation and thus conserves water resources and maintains soil quality.
In addition to optimizing irrigation, digital farming offers advanced solutions for other areas: The monitoring of cooling systems ensures the ideal storage of agricultural products, minimizing food losses and ensuring product quality. Level sensors in silos and warehouses enable efficient storage and inventory management, reduce overfilling and losses and optimize the supply chain.
In the field of animal husbandry, controlling the climate in the barn makes a decisive contribution to the well-being and health of the animals. By monitoring temperature, humidity and air quality, optimal conditions can be created that have a positive effect on productivity and animal health.
The integration of weather data in real time enables farmers to adapt work processes and proactively counter risks such as frost or heat damage. In addition, machine monitoring through digital farming enables predictive maintenance of agricultural machinery, reduces downtimes and increases the efficiency of machine use.
In summary, digital farming creates added value by optimizing agricultural production processes, using resources efficiently and promoting sustainable growth. By integrating digital technologies, farms can maximize their yields, reduce operating costs and contribute to environmental protection. The high added value through resource efficiency makes digital farming an indispensable part of modern agricultural practices.